Featured This Month
Pediatric and Neonatal Care
What Are Normal Weight and Height Milestones for Babies?
 Skyler
Skyler
 10 Mar 2026
10 Mar 2026
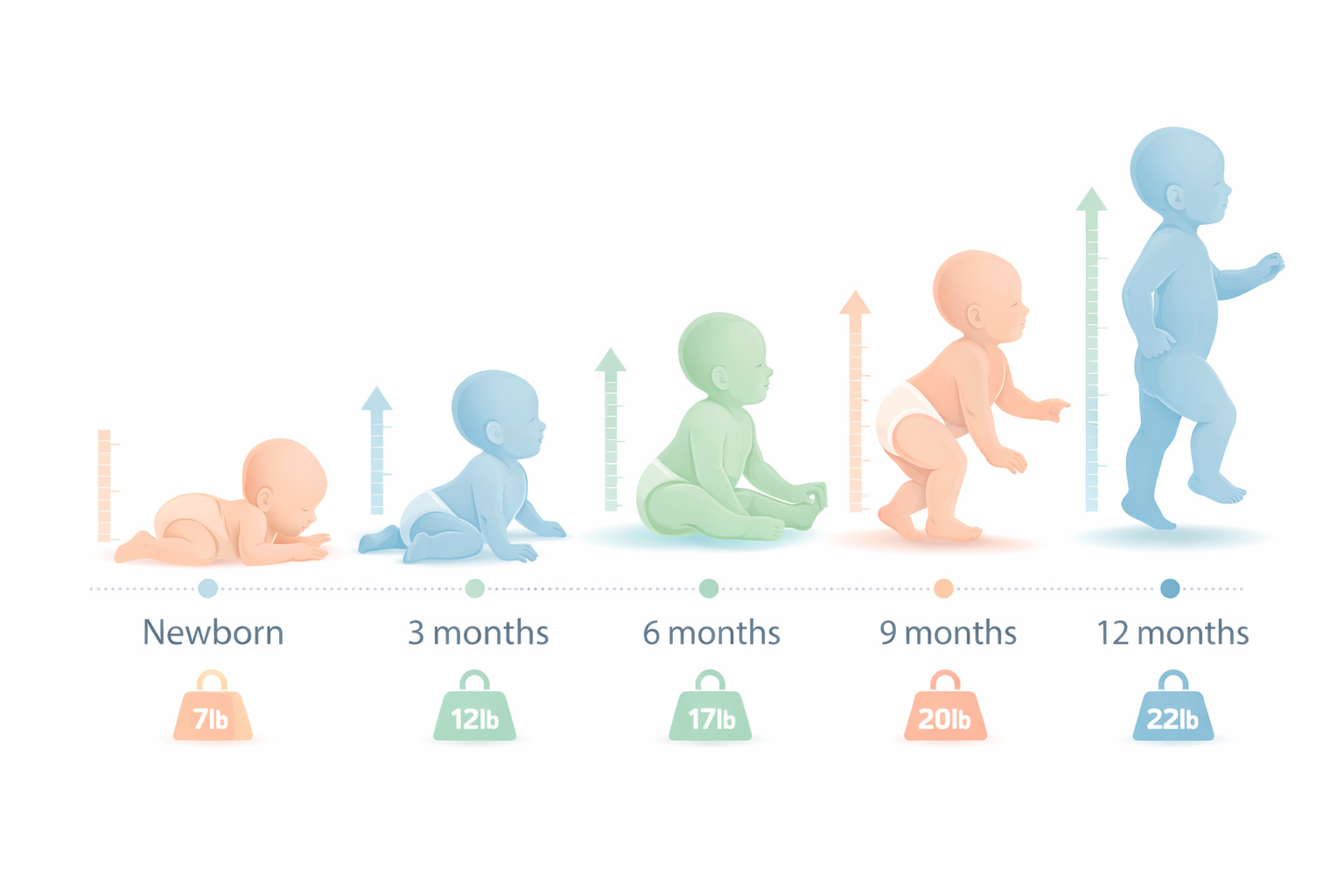
Understanding Infant Growth Charts and Healthy Development Stages What Are Normal Weight and Height Milestones for Babies? Normal baby weight and height milestones follow predictable patterns during the first year, although every baby grows at their own pace. Most infants double their birth weight by around 5 months and triple it by their first birthday, while growing roughly 10 inches (about 25 cm) in length during the first year. Pediatricians use a baby growth chart by age to track whether a baby’s weight and height are progressing in healthy ranges. For parents, those charts can sometimes look confusing. A baby might be in the 30th percentile one month and the 40th the next. That doesn’t automatically mean something is wrong. Growth during infancy isn’t perfectly smooth. It tends to come in bursts. Understanding the general baby growth milestones weight and height guide can make those checkups feel a lot less stressful. Average Baby Weight Milestones in the First Year The first year of life is when babies grow faster than at any other time. At birth, most full-term babies weigh somewhere between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5–4 kg). That range is considered normal. Some babies start smaller, some larger. What matters more is how steadily they grow afterward. A typical normal baby weight by month looks roughly like this: Birth: 5.5–8.8 pounds (2.5–4 kg) 1 month: around 8–10 pounds (3.6–4.5 kg) 3 months: about 12–15 pounds (5.4–6.8 kg) 5–6 months: most babies double their birth weight 9 months: usually 17–22 pounds (7.7–10 kg) 12 months: birth weight typically triples Weight gain tends to happen fastest during the first four to six months. Babies feed frequently during this stage and their bodies are growing rapidly. After about six months, growth slows a bit. That’s normal. Babies start moving more, rolling, crawling, and eventually pulling themselves up. Energy goes into development as much as growth. Typical Height Growth Milestones During the First Year Weight often gets the most attention, but length (or height) is just as important when doctors evaluate infant growth chart weight and height patterns. At birth, babies are usually around 19–21 inches long (48–53 cm). From there, the growth tends to follow a gradual pattern. Typical average baby height by month milestones look something like this: Birth: about 19–21 inches (48–53 cm) 3 months: around 23–24 inches (58–61 cm) 6 months: about 25–27 inches (63–69 cm) 9 months: around 26–28 inches (66–71 cm) 12 months: usually 28–30 inches (71–76 cm) During the first six months, babies often grow close to 1 inch per month. After that, the pace slows a little to roughly half an inch per month. Again, these numbers are general guidelines. Some babies grow slightly faster, others a bit slower. How Pediatricians Use Baby Growth Percentiles Doctors don’t rely on a single number when they look at baby growth standards by age. Instead, they use growth percentiles. Growth charts compare your baby with thousands of other children the same age. They measure several things: Weight-for-age Length-for-age Weight-for-length Head circumference A baby in the 25th percentile, for example, weighs more than 25% of babies their age and less than 75%. Some parents worry if their baby isn’t near the top of the chart. But that isn’t necessarily important. What pediatricians usually care about most is consistency. If a baby tracks along the same percentile line over time, that’s often a sign that growth is healthy. Growth Patterns During the First 12 Months One thing that surprises many new parents is that babies don’t grow in a straight line. Growth tends to happen in phases. There are periods where a baby suddenly seems bigger almost overnight. Then things slow down again. During the first few months, babies often gain weight rapidly. Feeding happens frequently, sometimes every two or three hours. After around six months, growth slows a little as babies begin exploring movement and starting solid foods. Parents often notice something else during the first year — growth spurts. These usually appear around: 2–3 weeks 6 weeks 3 months 6 months During these periods, babies may suddenly want to feed much more often. Sleep patterns can shift too. It can feel exhausting for parents, but growth spurts usually settle down after a few days. Factors That Influence a Baby’s Weight and Height Every baby grows differently, and there are several reasons why. Genetics play a big role. Parents who are naturally taller may have babies who grow taller as well. The same idea applies to body build. Other factors can also influence the baby growth chart by month weight and height pattern. These include: genetics and parental height premature birth feeding method (breastfeeding or formula) nutrition after introducing solids overall health sleep patterns activity level as babies begin moving more Because of these differences, two healthy babies can grow at completely different rates. That’s why pediatricians focus on growth trends rather than comparing babies to each other. Differences Between Breastfed and Formula-Fed Babies Parents sometimes worry when their baby’s growth pattern looks different from another child’s. Feeding method can influence early growth patterns slightly. Breastfed babies Often gain weight faster during the first 2–3 months Growth may slow slightly after around 6 months Formula-fed babies May gain weight more steadily throughout the year Both patterns can be completely normal. Doctors simply look for steady progress on the infant growth chart weight and height curves. Consistency matters more than speed. Signs That a Baby Is Growing Well Parents often notice certain signs that their baby is developing normally. Growth is usually reflected in everyday things. You might see: steady weight gain at pediatric checkups increasing appetite clothes and diapers becoming tight improved energy and alertness new physical milestones such as rolling, sitting, or crawling These signs generally indicate that nutrition and development are on track. Growth and development tend to move together during the first year. When Baby Growth May Need Medical Evaluation Most variations in growth are completely normal. But sometimes doctors want to take a closer look. Parents should speak with a healthcare professional if a baby: isn’t gaining weight over time stops growing in length drops noticeably on growth charts has persistent feeding problems seems unusually lethargic or dehydrated In many cases the cause may be simple — feeding challenges, reflux, or temporary illness. Early evaluation helps doctors identify issues before they become more serious. Supporting Healthy Weight and Height Development Parents don’t need to obsess over numbers to support healthy growth. Many of the most important things are surprisingly simple. Babies grow best when their basic needs are met consistently. Helpful habits include: feeding babies on demand during the early months introducing solid foods around 6 months, when recommended attending regular pediatric checkups allowing adequate sleep monitoring feeding patterns and hydration Routine well-baby visits allow healthcare providers to track growth and offer guidance based on the baby’s individual development. Those visits are often where doctors update the baby growth milestones chart and make sure everything is progressing normally. For most families, those growth charts become reassuring over time. They show that even when development feels unpredictable day-to-day, babies usually follow a healthy path forward.
Allergy and Immunology
How Long Does It Take for Claritin to Work?
 Ashlee
Ashlee
 06 Mar 2026
06 Mar 2026
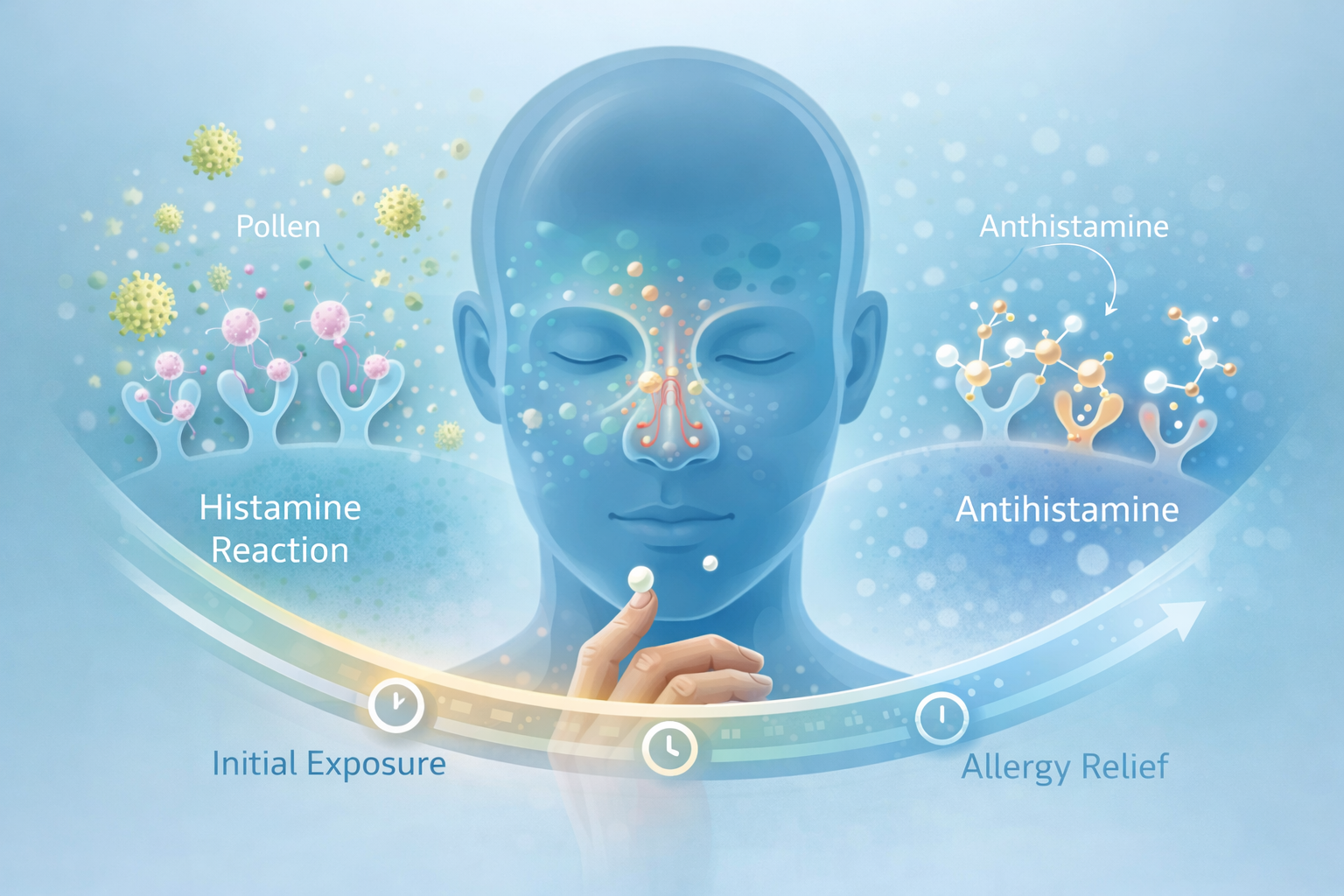
Claritin (Loratadine) Onset Time, Duration, and Allergy Relief Guide Claritin usually starts working within about 1 to 3 hours after you take it. Most people begin noticing their allergy symptoms easing the same day, and one dose typically keeps working for about 24 hours. Some people feel relief a little sooner, others a little later. That’s normal. If you’ve ever taken Claritin during allergy season, you probably know the feeling. Relief doesn’t usually hit all at once. It tends to come on gradually. The sneezing slows down. Your eyes itch less. Things just start calming down. Let’s talk through what’s actually happening after you take it. When Most People Start Feeling Allergy Relief If you're asking how long does Claritin take to work, the typical timing is fairly predictable. Most people start feeling something within 1 to 3 hours after taking a tablet. Not dramatic relief right away. More like small changes at first. Maybe you're sneezing less often.Maybe your nose isn’t running constantly anymore. The medication keeps building in your system through the day. Because of that, the strongest effect often shows up several hours later, usually somewhere around 8 to 12 hours after the dose. A simple way to think about it: First relief: about 1–3 hours Strongest effect: later in the day Total relief window: around 24 hours That’s why Claritin is usually taken once per day. Some people feel improvement a bit faster. Others need a few hours. Both are completely normal. The Allergy Symptoms Claritin Helps With Claritin is designed to calm down symptoms caused by histamine. Histamine is the chemical your body releases when it thinks something like pollen or pet dander is a threat. Once that chemical starts circulating, the classic allergy symptoms appear. Things like: Sneezing Runny nose Itchy nose Watery or itchy eyes Scratchy throat General seasonal allergy irritation If you deal with hay fever during spring or fall, this is exactly the kind of medication doctors often recommend. One thing to know though. Claritin can sometimes be less helpful for severe nasal congestion. That heavy “blocked sinus” feeling often comes from inflammation deeper in the nasal passages. Antihistamines don’t always fix that part completely. For congestion, some people end up needing an additional treatment. What’s Actually Happening Inside Your Body The active ingredient in Claritin is loratadine. It belongs to a group called second-generation antihistamines. These are newer allergy medications designed to reduce symptoms without making most people sleepy. Here’s the simple version of what happens after you take it. The tablet dissolves.Your body absorbs the medication through the digestive system.It enters the bloodstream. Once it’s circulating, loratadine starts blocking histamine receptors. Histamine is basically the signal that triggers allergy symptoms. Sneezing, itching, watery eyes — those are all responses to that signal. When Claritin blocks it, your body stops reacting as strongly. Your liver also converts loratadine into another compound called desloratadine, which continues helping block histamine for many hours. That’s part of why the medication lasts all day. Why Claritin Sometimes Works Faster for Some People Even though the usual Claritin onset time is about 1–3 hours, there are a few things that can make it feel faster or slower. Everyone’s body is a little different. A few factors that matter: How strong your allergies are Mild symptoms tend to calm down faster. If pollen levels are extremely high, relief may take longer. When you take the medication Taking Claritin before symptoms become intense often works better than waiting until allergies are already severe. Many people take it first thing in the morning during allergy season. Your metabolism Some people process medications faster than others. That can slightly affect how quickly Claritin works. Your allergen exposure If you're around pollen, dust, or pets constantly, symptoms can keep being triggered throughout the day. Reducing exposure often helps the medication work better. Does Claritin Work Better If You Take It Every Day? For occasional allergies, Claritin usually works the same day you take it. But during active allergy season, daily use can make symptom control much easier. Taking it consistently keeps histamine activity lower in your body. That means symptoms don’t have as much chance to build up. People often take Claritin daily when: pollen counts are high they spend time outside regularly seasonal allergies are active in their region Starting the medication before heavy allergen exposure can sometimes prevent symptoms from getting worse. What If Claritin Doesn't Seem to Be Working? This happens sometimes. Someone takes the medication and expects instant relief. Then after an hour they feel the same and assume it failed. Usually it just needs more time. If you're wondering how long before Claritin relieves allergy symptoms, it's important to wait a few hours before judging the result. If symptoms still aren’t improving, a few simple things can help. First, make sure you're taking the medication correctly. Claritin is usually taken once daily Taking extra doses won't make it work faster Second, try reducing allergen exposure. Things that help more than people expect: closing windows during high pollen days showering after spending time outdoors washing bedding regularly using air purifiers If symptoms are still stubborn after several days, it may be worth speaking with a pharmacist. If your doctor has recommended loratadine, it can be ordered through Sanford Pharmacy online, which allows you to receive your medication without waiting in pharmacy lines. Does Food Change How Quickly Claritin Works? This question comes up a lot. The short answer is no. Claritin can be taken with food or without food, and meals usually don’t change the Claritin allergy relief time very much. What matters more is taking it consistently. Many people take their dose in the morning, mainly so protection lasts throughout the day when pollen exposure is highest. Drug Presence vs Drug Effect Another small detail that confuses people. Even though Claritin may remain in your body longer than 24 hours, its symptom relief effect is designed to last about one day. That’s why doctors recommend one dose every 24 hours. Taking more won't necessarily improve symptoms faster. Consistency tends to work better. When It's Time to Ask a Pharmacist or Doctor Most allergy symptoms are manageable with medications like Claritin. But sometimes symptoms stick around longer than expected. You should talk with a healthcare professional if: allergy symptoms remain uncontrolled after several days severe sinus pressure develops fever appears along with allergy symptoms symptoms interfere with sleep or daily life you're taking other medications that could interact A pharmacist can often help figure out what’s going on. If you need help choosing an allergy treatment, a pharmacist at Sanford Pharmacy can review your symptoms and suggest appropriate options. Common Questions About Claritin Does Claritin work immediately?No. Most people begin noticing relief within 1 to 3 hours. How fast does Claritin work for seasonal allergies?Relief usually begins within a few hours, though the strongest effect may appear later in the day. Should Claritin be taken in the morning or at night?Many people take it in the morning so the medication works during the day when allergen exposure is higher. Does Claritin work immediately for allergies?No. Like most antihistamines, it needs time to circulate in the bloodstream. How long after taking Claritin do symptoms improve?Most people start noticing improvement within 1–3 hours, though full relief may take longer. When to Seek Medical Advice Most seasonal allergies respond well to antihistamines. Still, ongoing symptoms shouldn’t be ignored. You should seek medical advice if: allergy symptoms continue despite treatment breathing becomes difficult severe sinus pain develops symptoms resemble an infection instead of allergies If you've been prescribed loratadine and want a convenient way to receive your medication, Sanford Pharmacy offers online ordering so prescriptions can be delivered directly to your door. For many people, once the right allergy treatment is in place, relief usually isn’t far behind.

Allergy and Immunology
Does a Humidifier Help With Asthma?
 Simeon
Simeon
 04 Mar 2026
04 Mar 2026
Understanding Asthma and Airway Sensitivity People often ask does a humidifier help with asthma. The answer is not exactly yes or no. It depends on the air around you and how your lungs react to it. Asthma means the airways inside the lungs are sensitive. When something irritates them, they swell and narrow. The muscles around the airways tighten, and mucus can build up. When that happens, breathing can feel tight or heavy. Different things can trigger asthma symptoms. Some common triggers are: Dust and pollen Cigarette smoke Strong perfumes or chemicals Cold air Respiratory infections Very dry air Everyone’s triggers are a little different. For some people, dry air can irritate the throat and airways. That is why people sometimes wonder if a humidifier for asthma relief might help. Asthma management usually includes medication and avoiding triggers. Environmental changes, like adjusting humidity, can sometimes help reduce irritation in the airways. What a Humidifier Does A humidifier is a small device that adds moisture to the air in a room. Indoor air can become very dry, especially during winter. Heating systems remove moisture from the air. When the air gets dry enough, you might notice dry skin, dry throat, or irritated nasal passages. A humidifier releases water vapor into the air, raising the humidity level in the room. Some people feel that breathing becomes easier in slightly moist air. Because of this, many people ask is humidifier good for asthma or can humidifier improve asthma symptoms. The humidifier itself does not treat asthma. It simply changes the moisture level in the air you breathe. How Dry Air Affects Asthma Dry air can irritate the lining of the nose, throat, and airways. For people with asthma, the airways are already sensitive. When dry air passes through them, it can make irritation worse. Some people notice more coughing or throat scratchiness when the air is very dry. Cold winter air is often dry as well. When someone breathes in cold, dry air, the airways may tighten. That tightening can trigger coughing or wheezing. This is why some people begin looking into humidifier benefits for asthma. Moist air sometimes feels easier on irritated airways. However, not everyone with asthma reacts the same way. When a Humidifier May Help Asthma In very dry climates or heated homes during winter, a humidifier may make breathing more comfortable. For example, if someone wakes up with a dry throat or constant coughing caused by dry air, adding a little moisture to the room may help reduce irritation. Some people notice less coughing when the air is not extremely dry. Others say their throat feels less scratchy at night. This is one situation where humidifier vs asthma symptoms may show some improvement. Some people prefer a warm mist humidifier for asthma, especially during cold months. Warm mist can feel soothing to the throat. Others use cool mist models. The important point is that humidifiers may help with dryness, but they do not replace asthma medications. Potential Benefits of Using a Humidifier If used correctly and if the air in the home is very dry, a humidifier can have a few benefits. Possible effects include: Airways may feel less irritated Dry cough may improve Mucus may become thinner and easier to clear When airways are less irritated, breathing may feel more comfortable. That is why some people say they experience humidifier benefits for asthma during winter or in dry indoor environments. Still, the benefit varies. Some people feel no difference at all. When Humidifiers May Worsen Asthma Humidity that is too high can actually make asthma worse. This happens because high humidity encourages things that trigger asthma, such as: Mold growth Dust mites Both of these are common asthma triggers. Another issue is poor humidifier maintenance. If the device is not cleaned regularly, bacteria or mold can grow inside it. When the humidifier runs, those particles can spread into the air. Breathing in contaminated mist can irritate the lungs. Because of this, some homes with high humidity may need the opposite device. That is why people ask is a humidifier or dehumidifier better for asthma. In humid climates, lowering moisture may actually help more. Recommended Humidity Levels The goal is balance. Most experts recommend indoor humidity between 30% and 50%. Below 30% the air may feel dry and irritating. Above 50% the environment becomes ideal for mold and dust mites. A small device called a hygrometer can measure humidity levels in the room. Maintaining the right level helps people searching for the best humidity level for asthma. Tips for Safe Humidifier Use If someone chooses to use a humidifier, a few simple habits can make a big difference. Helpful tips include: Clean the humidifier regularly Change the water every day Use distilled or filtered water when possible Do not run the humidifier continuously without checking humidity levels Standing water inside the tank can allow bacteria or mold to grow. Cleaning prevents that problem. Also, over-humidifying a room can lead to damp air and mold growth. Monitoring humidity helps prevent this. These steps make humidifier for asthma relief safer for people who want to try it. Other Environmental Steps That Help Asthma Humidity is only one small part of asthma management. Other environmental steps often help more. For example: Using HEPA air purifiers to reduce allergens Keeping the home clean to reduce dust Washing bedding regularly Avoiding cigarette smoke Strong fragrances, aerosol sprays, and chemical cleaners can also irritate sensitive lungs. All these factors influence how humidity affects asthma symptoms. When to Seek Medical or Pharmacy Advice Environmental adjustments alone may not control asthma symptoms. Medical advice should be sought if: Wheezing becomes frequent Shortness of breath increases Asthma attacks happen more often Some people ask does using a humidifier help asthma attacks. The answer is no. Asthma attacks require proper medication, usually a rescue inhaler. Sanford Pharmacy can help explain asthma medications, inhaler technique, and ways to manage triggers at home. For many people with asthma, the best approach is a combination of medication, trigger control, and healthy indoor air conditions. Humidity can play a role, but it is only one part of the overall picture.

What Are Normal Weight and Height Milestones for Babies?
 Skyler
|
Skyler
|
 10 Mar 2026
10 Mar 2026

How Long Does It Take for Claritin to Work?
 Ashlee
|
Ashlee
|
 06 Mar 2026
06 Mar 2026

Does a Humidifier Help With Asthma?
 Simeon
|
Simeon
|
 04 Mar 2026
04 Mar 2026
What is Best Treatment for Arthritis in Lower Back?
 Myron
|
Myron
|
 02 Mar 2026
02 Mar 2026
What is Clarithromycin Used For?
 Abril
|
Abril
|
 27 Feb 2026
27 Feb 2026
Recently Posted

Pediatric and Neonatal Care
What Are Normal Weight and Height Milestones for Babies?
 Skyler
Skyler
 10 Mar 2026
10 Mar 2026
Understanding Infant Growth Charts and Healthy Development Stages What Are Normal Weight and Height Milestones for Babies? Normal baby weight and height milestones follow predictable patterns during the first year, although every baby grows at their own pace. Most infants double their birth weight by around 5 months and triple it by their first birthday, while growing roughly 10 inches (about 25 cm) in length during the first year. Pediatricians use a baby growth chart by age to track whether a baby’s weight and height are progressing in healthy ranges. For parents, those charts can sometimes look confusing. A baby might be in the 30th percentile one month and the 40th the next. That doesn’t automatically mean something is wrong. Growth during infancy isn’t perfectly smooth. It tends to come in bursts. Understanding the general baby growth milestones weight and height guide can make those checkups feel a lot less stressful. Average Baby Weight Milestones in the First Year The first year of life is when babies grow faster than at any other time. At birth, most full-term babies weigh somewhere between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5–4 kg). That range is considered normal. Some babies start smaller, some larger. What matters more is how steadily they grow afterward. A typical normal baby weight by month looks roughly like this: Birth: 5.5–8.8 pounds (2.5–4 kg) 1 month: around 8–10 pounds (3.6–4.5 kg) 3 months: about 12–15 pounds (5.4–6.8 kg) 5–6 months: most babies double their birth weight 9 months: usually 17–22 pounds (7.7–10 kg) 12 months: birth weight typically triples Weight gain tends to happen fastest during the first four to six months. Babies feed frequently during this stage and their bodies are growing rapidly. After about six months, growth slows a bit. That’s normal. Babies start moving more, rolling, crawling, and eventually pulling themselves up. Energy goes into development as much as growth. Typical Height Growth Milestones During the First Year Weight often gets the most attention, but length (or height) is just as important when doctors evaluate infant growth chart weight and height patterns. At birth, babies are usually around 19–21 inches long (48–53 cm). From there, the growth tends to follow a gradual pattern. Typical average baby height by month milestones look something like this: Birth: about 19–21 inches (48–53 cm) 3 months: around 23–24 inches (58–61 cm) 6 months: about 25–27 inches (63–69 cm) 9 months: around 26–28 inches (66–71 cm) 12 months: usually 28–30 inches (71–76 cm) During the first six months, babies often grow close to 1 inch per month. After that, the pace slows a little to roughly half an inch per month. Again, these numbers are general guidelines. Some babies grow slightly faster, others a bit slower. How Pediatricians Use Baby Growth Percentiles Doctors don’t rely on a single number when they look at baby growth standards by age. Instead, they use growth percentiles. Growth charts compare your baby with thousands of other children the same age. They measure several things: Weight-for-age Length-for-age Weight-for-length Head circumference A baby in the 25th percentile, for example, weighs more than 25% of babies their age and less than 75%. Some parents worry if their baby isn’t near the top of the chart. But that isn’t necessarily important. What pediatricians usually care about most is consistency. If a baby tracks along the same percentile line over time, that’s often a sign that growth is healthy. Growth Patterns During the First 12 Months One thing that surprises many new parents is that babies don’t grow in a straight line. Growth tends to happen in phases. There are periods where a baby suddenly seems bigger almost overnight. Then things slow down again. During the first few months, babies often gain weight rapidly. Feeding happens frequently, sometimes every two or three hours. After around six months, growth slows a little as babies begin exploring movement and starting solid foods. Parents often notice something else during the first year — growth spurts. These usually appear around: 2–3 weeks 6 weeks 3 months 6 months During these periods, babies may suddenly want to feed much more often. Sleep patterns can shift too. It can feel exhausting for parents, but growth spurts usually settle down after a few days. Factors That Influence a Baby’s Weight and Height Every baby grows differently, and there are several reasons why. Genetics play a big role. Parents who are naturally taller may have babies who grow taller as well. The same idea applies to body build. Other factors can also influence the baby growth chart by month weight and height pattern. These include: genetics and parental height premature birth feeding method (breastfeeding or formula) nutrition after introducing solids overall health sleep patterns activity level as babies begin moving more Because of these differences, two healthy babies can grow at completely different rates. That’s why pediatricians focus on growth trends rather than comparing babies to each other. Differences Between Breastfed and Formula-Fed Babies Parents sometimes worry when their baby’s growth pattern looks different from another child’s. Feeding method can influence early growth patterns slightly. Breastfed babies Often gain weight faster during the first 2–3 months Growth may slow slightly after around 6 months Formula-fed babies May gain weight more steadily throughout the year Both patterns can be completely normal. Doctors simply look for steady progress on the infant growth chart weight and height curves. Consistency matters more than speed. Signs That a Baby Is Growing Well Parents often notice certain signs that their baby is developing normally. Growth is usually reflected in everyday things. You might see: steady weight gain at pediatric checkups increasing appetite clothes and diapers becoming tight improved energy and alertness new physical milestones such as rolling, sitting, or crawling These signs generally indicate that nutrition and development are on track. Growth and development tend to move together during the first year. When Baby Growth May Need Medical Evaluation Most variations in growth are completely normal. But sometimes doctors want to take a closer look. Parents should speak with a healthcare professional if a baby: isn’t gaining weight over time stops growing in length drops noticeably on growth charts has persistent feeding problems seems unusually lethargic or dehydrated In many cases the cause may be simple — feeding challenges, reflux, or temporary illness. Early evaluation helps doctors identify issues before they become more serious. Supporting Healthy Weight and Height Development Parents don’t need to obsess over numbers to support healthy growth. Many of the most important things are surprisingly simple. Babies grow best when their basic needs are met consistently. Helpful habits include: feeding babies on demand during the early months introducing solid foods around 6 months, when recommended attending regular pediatric checkups allowing adequate sleep monitoring feeding patterns and hydration Routine well-baby visits allow healthcare providers to track growth and offer guidance based on the baby’s individual development. Those visits are often where doctors update the baby growth milestones chart and make sure everything is progressing normally. For most families, those growth charts become reassuring over time. They show that even when development feels unpredictable day-to-day, babies usually follow a healthy path forward.

Allergy and Immunology
How Long Does It Take for Claritin to Work?
 Ashlee
Ashlee
 06 Mar 2026
06 Mar 2026
Claritin (Loratadine) Onset Time, Duration, and Allergy Relief Guide Claritin usually starts working within about 1 to 3 hours after you take it. Most people begin noticing their allergy symptoms easing the same day, and one dose typically keeps working for about 24 hours. Some people feel relief a little sooner, others a little later. That’s normal. If you’ve ever taken Claritin during allergy season, you probably know the feeling. Relief doesn’t usually hit all at once. It tends to come on gradually. The sneezing slows down. Your eyes itch less. Things just start calming down. Let’s talk through what’s actually happening after you take it. When Most People Start Feeling Allergy Relief If you're asking how long does Claritin take to work, the typical timing is fairly predictable. Most people start feeling something within 1 to 3 hours after taking a tablet. Not dramatic relief right away. More like small changes at first. Maybe you're sneezing less often.Maybe your nose isn’t running constantly anymore. The medication keeps building in your system through the day. Because of that, the strongest effect often shows up several hours later, usually somewhere around 8 to 12 hours after the dose. A simple way to think about it: First relief: about 1–3 hours Strongest effect: later in the day Total relief window: around 24 hours That’s why Claritin is usually taken once per day. Some people feel improvement a bit faster. Others need a few hours. Both are completely normal. The Allergy Symptoms Claritin Helps With Claritin is designed to calm down symptoms caused by histamine. Histamine is the chemical your body releases when it thinks something like pollen or pet dander is a threat. Once that chemical starts circulating, the classic allergy symptoms appear. Things like: Sneezing Runny nose Itchy nose Watery or itchy eyes Scratchy throat General seasonal allergy irritation If you deal with hay fever during spring or fall, this is exactly the kind of medication doctors often recommend. One thing to know though. Claritin can sometimes be less helpful for severe nasal congestion. That heavy “blocked sinus” feeling often comes from inflammation deeper in the nasal passages. Antihistamines don’t always fix that part completely. For congestion, some people end up needing an additional treatment. What’s Actually Happening Inside Your Body The active ingredient in Claritin is loratadine. It belongs to a group called second-generation antihistamines. These are newer allergy medications designed to reduce symptoms without making most people sleepy. Here’s the simple version of what happens after you take it. The tablet dissolves.Your body absorbs the medication through the digestive system.It enters the bloodstream. Once it’s circulating, loratadine starts blocking histamine receptors. Histamine is basically the signal that triggers allergy symptoms. Sneezing, itching, watery eyes — those are all responses to that signal. When Claritin blocks it, your body stops reacting as strongly. Your liver also converts loratadine into another compound called desloratadine, which continues helping block histamine for many hours. That’s part of why the medication lasts all day. Why Claritin Sometimes Works Faster for Some People Even though the usual Claritin onset time is about 1–3 hours, there are a few things that can make it feel faster or slower. Everyone’s body is a little different. A few factors that matter: How strong your allergies are Mild symptoms tend to calm down faster. If pollen levels are extremely high, relief may take longer. When you take the medication Taking Claritin before symptoms become intense often works better than waiting until allergies are already severe. Many people take it first thing in the morning during allergy season. Your metabolism Some people process medications faster than others. That can slightly affect how quickly Claritin works. Your allergen exposure If you're around pollen, dust, or pets constantly, symptoms can keep being triggered throughout the day. Reducing exposure often helps the medication work better. Does Claritin Work Better If You Take It Every Day? For occasional allergies, Claritin usually works the same day you take it. But during active allergy season, daily use can make symptom control much easier. Taking it consistently keeps histamine activity lower in your body. That means symptoms don’t have as much chance to build up. People often take Claritin daily when: pollen counts are high they spend time outside regularly seasonal allergies are active in their region Starting the medication before heavy allergen exposure can sometimes prevent symptoms from getting worse. What If Claritin Doesn't Seem to Be Working? This happens sometimes. Someone takes the medication and expects instant relief. Then after an hour they feel the same and assume it failed. Usually it just needs more time. If you're wondering how long before Claritin relieves allergy symptoms, it's important to wait a few hours before judging the result. If symptoms still aren’t improving, a few simple things can help. First, make sure you're taking the medication correctly. Claritin is usually taken once daily Taking extra doses won't make it work faster Second, try reducing allergen exposure. Things that help more than people expect: closing windows during high pollen days showering after spending time outdoors washing bedding regularly using air purifiers If symptoms are still stubborn after several days, it may be worth speaking with a pharmacist. If your doctor has recommended loratadine, it can be ordered through Sanford Pharmacy online, which allows you to receive your medication without waiting in pharmacy lines. Does Food Change How Quickly Claritin Works? This question comes up a lot. The short answer is no. Claritin can be taken with food or without food, and meals usually don’t change the Claritin allergy relief time very much. What matters more is taking it consistently. Many people take their dose in the morning, mainly so protection lasts throughout the day when pollen exposure is highest. Drug Presence vs Drug Effect Another small detail that confuses people. Even though Claritin may remain in your body longer than 24 hours, its symptom relief effect is designed to last about one day. That’s why doctors recommend one dose every 24 hours. Taking more won't necessarily improve symptoms faster. Consistency tends to work better. When It's Time to Ask a Pharmacist or Doctor Most allergy symptoms are manageable with medications like Claritin. But sometimes symptoms stick around longer than expected. You should talk with a healthcare professional if: allergy symptoms remain uncontrolled after several days severe sinus pressure develops fever appears along with allergy symptoms symptoms interfere with sleep or daily life you're taking other medications that could interact A pharmacist can often help figure out what’s going on. If you need help choosing an allergy treatment, a pharmacist at Sanford Pharmacy can review your symptoms and suggest appropriate options. Common Questions About Claritin Does Claritin work immediately?No. Most people begin noticing relief within 1 to 3 hours. How fast does Claritin work for seasonal allergies?Relief usually begins within a few hours, though the strongest effect may appear later in the day. Should Claritin be taken in the morning or at night?Many people take it in the morning so the medication works during the day when allergen exposure is higher. Does Claritin work immediately for allergies?No. Like most antihistamines, it needs time to circulate in the bloodstream. How long after taking Claritin do symptoms improve?Most people start noticing improvement within 1–3 hours, though full relief may take longer. When to Seek Medical Advice Most seasonal allergies respond well to antihistamines. Still, ongoing symptoms shouldn’t be ignored. You should seek medical advice if: allergy symptoms continue despite treatment breathing becomes difficult severe sinus pain develops symptoms resemble an infection instead of allergies If you've been prescribed loratadine and want a convenient way to receive your medication, Sanford Pharmacy offers online ordering so prescriptions can be delivered directly to your door. For many people, once the right allergy treatment is in place, relief usually isn’t far behind.

Allergy and Immunology
Does a Humidifier Help With Asthma?
 Simeon
Simeon
 04 Mar 2026
04 Mar 2026
Understanding Asthma and Airway Sensitivity People often ask does a humidifier help with asthma. The answer is not exactly yes or no. It depends on the air around you and how your lungs react to it. Asthma means the airways inside the lungs are sensitive. When something irritates them, they swell and narrow. The muscles around the airways tighten, and mucus can build up. When that happens, breathing can feel tight or heavy. Different things can trigger asthma symptoms. Some common triggers are: Dust and pollen Cigarette smoke Strong perfumes or chemicals Cold air Respiratory infections Very dry air Everyone’s triggers are a little different. For some people, dry air can irritate the throat and airways. That is why people sometimes wonder if a humidifier for asthma relief might help. Asthma management usually includes medication and avoiding triggers. Environmental changes, like adjusting humidity, can sometimes help reduce irritation in the airways. What a Humidifier Does A humidifier is a small device that adds moisture to the air in a room. Indoor air can become very dry, especially during winter. Heating systems remove moisture from the air. When the air gets dry enough, you might notice dry skin, dry throat, or irritated nasal passages. A humidifier releases water vapor into the air, raising the humidity level in the room. Some people feel that breathing becomes easier in slightly moist air. Because of this, many people ask is humidifier good for asthma or can humidifier improve asthma symptoms. The humidifier itself does not treat asthma. It simply changes the moisture level in the air you breathe. How Dry Air Affects Asthma Dry air can irritate the lining of the nose, throat, and airways. For people with asthma, the airways are already sensitive. When dry air passes through them, it can make irritation worse. Some people notice more coughing or throat scratchiness when the air is very dry. Cold winter air is often dry as well. When someone breathes in cold, dry air, the airways may tighten. That tightening can trigger coughing or wheezing. This is why some people begin looking into humidifier benefits for asthma. Moist air sometimes feels easier on irritated airways. However, not everyone with asthma reacts the same way. When a Humidifier May Help Asthma In very dry climates or heated homes during winter, a humidifier may make breathing more comfortable. For example, if someone wakes up with a dry throat or constant coughing caused by dry air, adding a little moisture to the room may help reduce irritation. Some people notice less coughing when the air is not extremely dry. Others say their throat feels less scratchy at night. This is one situation where humidifier vs asthma symptoms may show some improvement. Some people prefer a warm mist humidifier for asthma, especially during cold months. Warm mist can feel soothing to the throat. Others use cool mist models. The important point is that humidifiers may help with dryness, but they do not replace asthma medications. Potential Benefits of Using a Humidifier If used correctly and if the air in the home is very dry, a humidifier can have a few benefits. Possible effects include: Airways may feel less irritated Dry cough may improve Mucus may become thinner and easier to clear When airways are less irritated, breathing may feel more comfortable. That is why some people say they experience humidifier benefits for asthma during winter or in dry indoor environments. Still, the benefit varies. Some people feel no difference at all. When Humidifiers May Worsen Asthma Humidity that is too high can actually make asthma worse. This happens because high humidity encourages things that trigger asthma, such as: Mold growth Dust mites Both of these are common asthma triggers. Another issue is poor humidifier maintenance. If the device is not cleaned regularly, bacteria or mold can grow inside it. When the humidifier runs, those particles can spread into the air. Breathing in contaminated mist can irritate the lungs. Because of this, some homes with high humidity may need the opposite device. That is why people ask is a humidifier or dehumidifier better for asthma. In humid climates, lowering moisture may actually help more. Recommended Humidity Levels The goal is balance. Most experts recommend indoor humidity between 30% and 50%. Below 30% the air may feel dry and irritating. Above 50% the environment becomes ideal for mold and dust mites. A small device called a hygrometer can measure humidity levels in the room. Maintaining the right level helps people searching for the best humidity level for asthma. Tips for Safe Humidifier Use If someone chooses to use a humidifier, a few simple habits can make a big difference. Helpful tips include: Clean the humidifier regularly Change the water every day Use distilled or filtered water when possible Do not run the humidifier continuously without checking humidity levels Standing water inside the tank can allow bacteria or mold to grow. Cleaning prevents that problem. Also, over-humidifying a room can lead to damp air and mold growth. Monitoring humidity helps prevent this. These steps make humidifier for asthma relief safer for people who want to try it. Other Environmental Steps That Help Asthma Humidity is only one small part of asthma management. Other environmental steps often help more. For example: Using HEPA air purifiers to reduce allergens Keeping the home clean to reduce dust Washing bedding regularly Avoiding cigarette smoke Strong fragrances, aerosol sprays, and chemical cleaners can also irritate sensitive lungs. All these factors influence how humidity affects asthma symptoms. When to Seek Medical or Pharmacy Advice Environmental adjustments alone may not control asthma symptoms. Medical advice should be sought if: Wheezing becomes frequent Shortness of breath increases Asthma attacks happen more often Some people ask does using a humidifier help asthma attacks. The answer is no. Asthma attacks require proper medication, usually a rescue inhaler. Sanford Pharmacy can help explain asthma medications, inhaler technique, and ways to manage triggers at home. For many people with asthma, the best approach is a combination of medication, trigger control, and healthy indoor air conditions. Humidity can play a role, but it is only one part of the overall picture.

Analgesics and Anti-inflammatory
What is Best Treatment for Arthritis in Lower Back?
 Myron
Myron
 02 Mar 2026
02 Mar 2026
Understanding Lower Back Arthritis Lower back arthritis is usually “wear and tear” in the joints of the lower spine. Most of the time, it’s osteoarthritis, sometimes mixed with degenerative disc disease. People often imagine one “bad disc,” but a lot of the pain comes from small joints in the back of the spine called facet joints. Those joints are like hinges. They let you bend and twist. Over years, the smooth lining (cartilage) can thin out. When that cushion is thinner, the joint gets irritated more easily. That irritation shows up as stiffness, aching, and sometimes a sharp catch when you move a certain way. So the best treatment for arthritis in lower back is rarely one magic thing. It’s usually a few pieces done consistently: moving more (but the right kind), building support muscles, managing flare-ups, and using medicine carefully when needed. That’s the core of good lower back arthritis treatment. Common symptoms of lower back Arthritis Lower back arthritis tends to feel predictable. Not always, but often. Common symptoms: A dull ache in the low back that sticks around Stiffness when you get out of bed or after sitting Pain that ramps up with prolonged standing, bending, or repeated lifting Feeling “tight” or less flexible through the day Some people feel better once they warm up, then worse again after too much activity Arthritis pain is often worse at the end of a long day. Muscle strain is often worse right after one incident. That difference isn’t perfect, but it helps people understand what’s going on. If pain shoots down the leg, that can still happen with arthritis, but it often means a nerve is irritated too. That’s when you start thinking about a medical evaluation sooner. First-line treatment: lifestyle modifications If you look at how to treat arthritis in lower back, this is where most people start, and honestly where most improvement happens. Weight (if relevant):Extra weight isn’t “the cause” of arthritis, but it does increase load. The lower back is a load-bearing area. Even a small reduction can reduce daily stress on joints. Sitting less, breaking it up:Long sitting compresses the low back and tightens hip flexors. Even if you have a desk job, try a pattern like: stand up every 30–60 minutes walk for 1–2 minutes do a gentle back bend or hip stretch (nothing aggressive) Posture and ergonomics:This doesn’t mean “sit perfectly straight all day.” That’s tiring. It means reduce obvious strain: feet flat screen at eye level lower back supported avoid leaning forward with your head/neck for long periods Daily movement habit:Arthritic joints generally hate two things: too much load, and too much stillness. Gentle movement is like oil for a hinge. You’re trying to keep the hinge moving without forcing it. These are boring steps, but they’re often the foundation of lumbar spine arthritis pain management. Physical Therapy If you want a “superhuman” explanation, here’s the simple truth: the spine is not meant to be held up by bones and joints alone. It’s meant to be supported by muscle. Physical therapy for lumbar arthritis usually targets: Core strength (front and sides of abdomen) Glutes and hips (huge for taking load off the low back) Small stabilizers around the spine Flexibility in hips and hamstrings (tight hips make the low back do extra work) A good PT program isn’t just “do these exercises.” It teaches: How to hinge at the hips instead of rounding the lower back How to get up from a chair without twisting poorly How to lift and carry without loading irritated joints A lot of people feel pain relief from PT not because arthritis disappears, but because the joints are no longer taking the full hit of every movement. Heat and cold therapy These sound too simple, but they help many people. Heat is usually better for stiffness: morning stiffness tight muscles “I feel locked up” Heat relaxes muscle guarding. When your back hurts, muscles tighten to protect you. Heat helps those muscles let go. Cold is often better for flare-ups: after you overdid activity swelling-type soreness hot, irritated feeling If you’re not sure: heat before activity to loosen cold after activity if it’s irritated This fits under natural remedies for lower back arthritis that are safe and practical. Over-the-counter pain relief For many people, OTC options are part of medicine for lower back arthritis, especially during flare days. Acetaminophen can help pain but doesn’t reduce inflammation. It’s sometimes a good first step for mild pain. NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen help pain and inflammation. They can be useful if inflammation is a big part of your flare. Important cautions (because this matters): NSAIDs can irritate the stomach and raise bleeding risk they can affect kidneys they can raise blood pressure in some people they interact with certain blood thinners and other meds Topical gels/creams (like anti-inflammatory gels) can help if pain feels superficial or localized. They won’t “fix” arthritis, but they can take the edge off without as much whole-body exposure. If you’re unsure what is safe with your health conditions and current meds, Sanford Pharmacy can review what you’re taking and help you choose an option that fits your situation. Prescription medications Prescription options vary because not every back pain pattern is the same. Depending on the situation, a clinician might consider: stronger anti-inflammatory meds for a short period muscle relaxants if muscle spasm is a major feature (usually short-term) nerve pain medicines if there’s nerve irritation (more leg symptoms) limited short-term pain meds in select cases (not a long-term plan) Corticosteroid injections can be helpful in certain cases: facet injections (if the facet joints are confirmed pain source) epidural steroid injections (more for nerve irritation) Injections can reduce inflammation and calm a flare, but they don’t rebuild cartilage. They are usually used to create a window where you can move better and build strength. Exercise and movement programs This is where many people either get better or get stuck. Because doing nothing feels safe, but it often makes arthritis worse long term. The best exercises for arthritis in lower back are usually low-impact and repeatable: Walking simple adjustable (10 minutes counts) improves blood flow and keeps joints moving Swimming or water walking water supports body weight movement without heavy load great for people who flare with land exercise Core work (gentle, controlled) dead bug variations bird dog side planks (modified)These teach the trunk to stabilize without forcing painful ranges. Hip and glute strengthening bridges clamshells step-ups (small step)Strong hips reduce how much the low back has to “do everything.” Stretching hip flexor stretch hamstring stretch (gentle) piriformis/hip stretchThis reduces pull on the low back. The key is consistency. Ten minutes daily beats one intense workout once a week. If you want long-term improvement, this is often the biggest part of lower back osteoarthritis treatment. Advanced treatment options If conservative care fails, there are other options. These are typically considered after a solid attempt at PT, exercise, and medication management. Epidural steroid injections (more nerve-related pain) Nerve blocks (can help confirm pain source) Radiofrequency ablation in some cases (targets pain signals from certain facet joints) Surgery is usually not the first answer for arthritis-only pain. It may be considered if there’s a severe structural issue, progressive nerve deficits, or pain that does not respond to well-done conservative care. These fall under lumbar arthritis treatment options beyond the basics. When to seek medical evaluation Get checked sooner (not later) if you have: pain radiating down the leg with numbness or weakness worsening weakness in the foot/leg numbness in the groin/saddle area loss of bladder or bowel control (emergency) fever with back pain, or unexplained weight loss pain after a major fall/trauma Also get evaluated if: symptoms are not improving after a few weeks of consistent conservative care pain is steadily worsening you can’t function day to day Role of ongoing support Most people do best when they treat this like a long-term condition with a plan, not a one-time crisis. Helpful ongoing steps: periodic check-ins with a clinician keeping an exercise routine even when you feel better using meds only as needed and safely learning your flare triggers (standing too long, long car rides, heavy lifting, poor sleep) Sanford Pharmacy can help with: picking an appropriate OTC option (acetaminophen vs NSAID vs topical) checking interactions with your current medicines helping you use pain relief products safely (heat wraps, topical gels, supports)

Bacterial and Fungal Infection
What is Clarithromycin Used For?
 Abril
Abril
 27 Feb 2026
27 Feb 2026
What Clarithromycin is When people ask what is clarithromycin used for, the answer is simple. It is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Clarithromycin belongs to a group of antibiotics called macrolides. It works differently from penicillin-type antibiotics. Because of that, it is sometimes used when other antibiotics are not suitable. It is available in: Immediate-release tablets Extended-release tablets Oral suspension for children The dose and form depend on the type of infection and the patient’s age. When people search what is clarithromycin used for in adults, it usually relates to respiratory or skin infections. How Clarithromycin Works Clarithromycin stops bacteria from making the proteins they need to grow. Without these proteins, bacteria cannot multiply properly. It does not instantly kill all bacteria. Instead, it slows or stops their growth. This gives the immune system time to clear the infection. It is effective against certain bacteria that cause: Respiratory infections Skin infections Some stomach infections This explains many common clarithromycin antibiotic uses. Respiratory Tract Infections One of the main clarithromycin uses is for respiratory infections. These include: Bronchitis Pneumonia Sinus infections Throat infections Clarithromycin for respiratory infection is often prescribed when bacteria are suspected rather than a virus. For example, clarithromycin uses for sinus infection may apply when symptoms are severe, prolonged, or worsening. It is important to remember that it does not treat viral colds. Ear Infections Clarithromycin may be used for acute otitis media in children. It is usually not the first choice, but it may be used when: The child cannot take penicillin Certain bacteria are suspected Parents often ask clarithromycin treats what infections when it is prescribed for ear pain. The answer depends on whether the infection is bacterial. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Clarithromycin can treat mild to moderate skin infections. These include: Cellulitis Infected cuts or wounds Certain soft tissue infections This is part of its role as clarithromycin for bacterial infection. Skin infections must be properly evaluated to determine if an antibiotic is needed. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Treatment Clarithromycin is also used in stomach ulcer treatment. It is part of combination therapy to treat H. pylori, a bacteria that can cause ulcers. In this case: It is taken with other antibiotics It is taken with acid-reducing medication It is not used alone for ulcers. The treatment usually lasts a set period based on medical guidelines. Certain Sexually Transmitted Infections In specific cases, clarithromycin may be used for certain infections if directed by a healthcare provider. It is not first-line for all sexually transmitted infections. Use depends on: The type of bacteria Sensitivity testing Medical judgment This is part of answering what infections does clarithromycin treat. Atypical Bacterial Infections Clarithromycin is active against some less common bacteria. Examples include: Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chlamydia pneumoniae Some non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections These are often called atypical infections. Macrolide antibiotics are sometimes chosen for these. When Clarithromycin Is Chosen Doctors may choose clarithromycin when: A patient has a penicillin allergy Bacteria are known to respond to it Culture results suggest susceptibility Dose matters. For example, clarithromycin 500 mg used for more serious infections or certain treatment plans. The clarithromycin dosage and duration for infection depends on the condition being treated. It must be taken exactly as prescribed. What Clarithromycin Does Not Treat Clarithromycin does not treat: Viral infections like colds or flu Fungal infections Bacteria that are resistant to it Using antibiotics for viral infections does not help and may increase resistance. Clarithromycin Side Effects and Uses Like all antibiotics, clarithromycin can cause side effects. Common side effects include: Nausea Diarrhea Metallic taste Less common but more serious side effects include: Heart rhythm changes Severe diarrhea Allergic reactions Understanding clarithromycin side effects and uses helps patients know what to expect. When to Seek Medical or Pharmacy Advice Medical advice should be sought if: Symptoms do not improve within 48 to 72 hours Severe diarrhea develops Irregular heartbeat occurs Rash or swelling appears Questions about clarithromycin dosage and duration for infection or potential drug interactions can be discussed with Sanford Pharmacy. Sanford Pharmacy can provide guidance on safe antibiotic use, timing, possible interactions, and what to do if a dose is missed. Clarithromycin is used for specific bacterial infections. It is not a general treatment for all illnesses. Proper diagnosis and correct dosing are important to ensure the infection is treated effectively and safely.
Women’s Health
How Long Does Premarin Stay in Your System?
 Annalise
Annalise
 25 Feb 2026
25 Feb 2026
What Premarin Is and Why It Is Prescribed How long does Premarin stay in your system is a common question, especially when someone is planning to stop hormone therapy. The short answer is that most of the medication leaves the bloodstream within a few days, but the body’s hormonal effects may last longer. Premarin is a form of conjugated estrogens. It is a type of hormone therapy. It is most often prescribed for menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It may also be used for certain hormonal deficiencies or after surgical removal of the ovaries. Premarin is available in several forms: Oral tablets Vaginal cream Injectable forms in specific situations The way it is taken affects premarin duration in body and overall hormone levels. How Premarin Works in the Body Premarin supplements or replaces estrogen levels in the body. During menopause, estrogen production decreases. This can lead to symptoms that affect comfort and quality of life. Estrogen affects many tissues, including: Reproductive organs Bones Brain Blood vessels The effects of Premarin depend on: Dose How long it is used Route of administration This is part of understanding premarin metabolism and how it behaves in the body. Half-Life of Premarin Premarin contains multiple estrogen compounds. Each one has a slightly different half-life. The average effective premarin half life is about 12 to 24 hours. Half-life means the time it takes for half of the drug to leave the bloodstream. Because it contains several estrogen forms, overall activity can vary slightly between individuals. Some metabolites may remain active longer than others. When discussing premarin half life in postmenopausal women, the general range is similar, though metabolism can vary with age. How Long Premarin Stays in Your System Most circulating estrogen levels decline within 1 to 3 days after stopping oral therapy. So, how long does premarin stay in your system after stopping? In most healthy individuals: Blood levels drop significantly within a few days Small amounts of metabolites may remain for several more days Nearly all of the drug is cleared within several days, though exact timing varies. If asking how long does premarin take to leave your body completely, the answer is usually within a few days for the drug itself, assuming normal liver function. Vaginal forms typically have lower systemic absorption. They generally clear faster from the bloodstream. How the Body Eliminates Premarin Premarin is metabolized primarily by the liver. After processing, estrogen metabolites are excreted through: Urine Bile Some estrogen undergoes enterohepatic recycling. This means it can be reabsorbed from the intestines before being fully eliminated. This can slightly prolong premarin clearance time, but usually not for an extended period. When people ask how long does estrogen stay in your system, it depends on the specific form and the individual’s metabolism. Factors That Affect Clearance Time Several factors influence premarin elimination time: Dose strength Duration of therapy Liver function Age Overall metabolic rate Oral versus vaginal use Higher doses or long-term use may result in slightly longer clearance. Individuals with liver impairment may experience slower premarin clearance time. Difference Between Drug Clearance and Hormonal Effects This is an important point. The medication may leave the bloodstream within days. However, hormonal effects may last longer. After stopping: Hot flashes may gradually return Vaginal dryness may slowly reappear Mood changes may occur temporarily This does not mean the drug is still active in high levels. It means the body is adjusting. So, how long does premarin last in the body can mean two different things: How long the drug is measurable How long the hormonal effects are felt The drug clears first. Symptoms may change gradually afterward. Side Effects After Stopping Premarin Some side effects improve quickly after stopping. These may include: Breast tenderness Mild bloating Fluid retention These often resolve within several days as estrogen levels decline. Hormonal fluctuations can cause temporary symptoms during adjustment. Persistent or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Special Considerations Long-term hormone therapy should not be stopped abruptly without discussion in some cases. Some individuals may be advised to taper gradually. This can reduce sudden hormonal shifts. Response varies. Some people notice quick changes. Others adjust slowly. Questions about how long does premarin stay in urine for drug test are uncommon in medical practice, as Premarin is not typically screened in routine drug testing. When present in urine, estrogen metabolites generally clear within several days after stopping. When to Seek Medical or Pharmacy Guidance Medical or pharmacy advice should be sought if: There are questions about stopping hormone therapy Side effects continue after discontinuation Symptoms return suddenly or severely Sanford Pharmacy can help answer questions about how long does premarin stay in your system, safe discontinuation, hormone therapy duration, and proper use. Understanding premarin duration in body helps set realistic expectations. In most healthy individuals, the medication itself clears within a few days. Hormonal effects may take longer to adjust as the body rebalances.
Popular Medicines





.webp)
.webp)
-(2).webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
_1.webp)
-(1).webp)
.webp)
.webp)